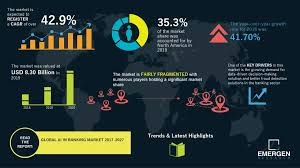
Based on the article, here’s an analysis of the AI landscape in financial services with specific application to Singapore:
Current State of AI in Singapore’s Financial Services
Clik here to view.

Singapore is positioning itself as a fintech hub, with the Singapore Fintech Festival serving as a platform for industry leaders to discuss AI implementation. Trust Bank and GXS Bank, mentioned in the article, represent Singapore-based financial institutions actively engaging with AI technologies.
Key Challenges for Singapore Banks
- Talent and Expertise Gap: As Trust Bank’s CEO noted, there is a shortage of genuine AI expertise despite widespread superficial knowledge.
- Data Management: Singapore banks face difficulties in accessing and utilizing their vast data stores, particularly in determining data quality for AI model training.
- Governance and Regulation: GXS Bank’s Chief Data Officer highlighted the need for clear guidelines on data access, privacy, and evaluation of AI-generated outputs in Singapore’s highly regulated financial environment.
- Balancing Innovation with Commercial Viability: Given limited resources, finding the right prioritization for AI investments is crucial, especially in Southeast Asian markets like Singapore.
Clik here to view.

Strategic Approaches for Singapore Financial Institutions
- Value-First Framework: Trust Bank’s “value prism” approach prioritizes use cases based on value and feasibility before committing resources.
- Pragmatic Implementation: Starting with clear business outcomes, thinking big but starting small, and scaling fast with robust governance frameworks.
- Leverage Existing Tools: Singapore banks are advised to explore existing AI tools before building everything from scratch.
- Maintain Flexibility: Given the rapid pace of AI development, Singapore financial institutions should avoid locking into specific platforms too early.
Clik here to view.

Promising Use Cases for Singapore
- Hyper-Personalization: Leveraging Singapore’s comprehensive digital ecosystem to gain holistic customer views and deliver tailored experiences.
- Fraud and Scam Prevention: Using AI to protect customers in Singapore’s digital banking environment by providing tools and behavioral nudges.
- Unstructured Data Analysis: Analyzing documents and images to combat fraud, particularly relevant in Singapore’s multilingual context.
- Voice Bots for Customer Service: Implementations like debt collection bots have shown success in driving cost efficiencies while maintaining quality service.
Clik here to view.

Singapore’s Position in the AI Hype Cycle
Singapore banks appear to be taking a measured approach. They acknowledge AI’s benefits while maintaining realistic expectations and focusing on demonstrable commercial value. The emphasis is on augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them, which aligns with Singapore’s focus on workforce transformation rather than displacement.
Regulatory Considerations
Singapore’s strong regulatory framework for financial services means that banks must adhere to principles of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency in AI implementations. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has been proactive in providing guidelines for responsible AI use in the financial sector.
Clik here to view.

Singapore’s Strategic Position in the Global AI Shift
Singapore has positioned itself strategically in the global AI landscape, leveraging several key advantages:
Geographical and Economic Advantages
Clik here to view.

- Strategic Location in Asia: Singapore serves as a gateway between East and West, positioned ideally to connect AI innovations from North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Financial Hub Status: Singapore’s established position as a financial center in Asia makes it a natural testbed for AI applications in finance, as evidenced by the presence of institutions like Trust Bank and GXS Bank, mentioned in the article.
- ASEAN Access: Singapore provides companies with access to the broader Southeast Asian market of over 650 million people, allowing AI solutions to be developed locally and scaled regionally.
Policy and Regulatory Environment
Clik here to view.

- Forward-looking Governance: Singapore has developed AI governance frameworks that balance innovation with responsible use, making it attractive for companies concerned about regulatory clarity.
- National AI Strategy: Singapore launched its National AI Strategy in 2019 (updated in 2023), demonstrating government commitment to AI development with a specific focus on finance as a key sector.
- Sandbox Environments: The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) provides regulatory sandboxes for fintech and AI experimentation, allowing controlled innovation in financial services.
Clik here to view.

Talent and Research Ecosystem
- AI Research Centers: Singapore hosts numerous AI research centers from global tech companies and universities, creating a concentration of expertise.
- Talent Development: Singapore’s education system and immigration policies are designed to develop and attract AI talent, addressing the expertise gap mentioned in the article.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government agencies, academic institutions, and private companies creates a cohesive AI ecosystem.
Clik here to view.

Infrastructure and Investment
- Digital Infrastructure: Singapore offers world-class digital infrastructure, high connectivity, and robust data centers, which are essential for AI development.
- Government Investment: Significant government funding for AI research and development through initiatives like AI Singapore.
- Venture Capital Access: Singapore’s mature financial ecosystem provides access to capital for AI startups and scale-ups.
Challenges in the Global Context
Clik here to view.

- Competition with Larger Markets: Singapore faces competition from more significant AI hubs like Silicon Valley, Beijing, and emerging centers in Europe.
- Scale Limitations: Despite its regional position, Singapore’s domestic market is relatively small, requiring companies to think regionally from the start.
- Balancing Act: As highlighted in the article, Singapore must balance innovation with governance and ethical considerations in AI development.
Clik here to view.

Singapore’s strategic approach positions it as a significant node in the global AI network, particularly for financial services applications. It leverages its strengths in governance, infrastructure, and regional connectivity while addressing challenges related to talent and scale.
AI’s Transformative Impact
The seminar emphasized that artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, is fundamentally reshaping financial and business landscapes. Industry leaders view AI as a game-changing technology that offers both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges for organizations of all sizes.
Clik here to view.

Perspectives from Industry Leaders
Pochara Arayakarnkul (Bluebik CEO) highlighted four critical AI applications in finance:
Enhancing customer interfaces
Streamlining back-office operations
Bolstering fraud detection
Driving product innovation
He particularly noted AI’s potential to:
Identify anomalies and suspicious behaviors beyond human detection
Enable hyper-personalized financial services
Improve funding access for underserved groups
Thadpong Pongthawornkamol (KBTG Managing Director) emphasized AI’s accessibility, stating that “everyone can access and interact with AI without needing to be a programmer.” He outlined four key areas for banking AI:
Enhancing customer service
Improving risk management
Boosting operational efficiency
Creating innovative financial products
Microsoft’s Perspective
Dhanawat Suthampun from Microsoft Thailand shared additional insights:
Over 75% of leading organizations are already leveraging generative AI
AI is unlocking unprecedented access to knowledge and insights
The technology has potential beyond business, including addressing global challenges and promoting sustainability
Strategic Implications
The seminar presented a clear message: Organizations must adapt to AI or risk being left behind. There’s particular excitement about Thailand’s potential to become a regional AI hub by creating impactful use cases.
Future Outlook
The consensus is that the “future of finance will belong to those who can harness AI’s potential to deliver seamless, proactive customer experiences.”
The article portrays AI not just as a technological tool but as a catalyst for profound change across industries, with particular transformative potential in finance and business.
AI Transformation in Finance and Business: Key Dimensions
1. Technological Disruption Landscape
Fundamental Shifts
- AI is not merely an incremental technological upgrade but a fundamental reimagining of business and financial processes.
- Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) are driving unprecedented innovation.
- Organizations face a binary choice: adapt and thrive or risk obsolescence
Accessibility and Democratization
- AI technologies are becoming increasingly accessible
- No longer restricted to large corporations or technical experts
- Enables smaller fintech companies to compete with established financial institutions
- Levels the playing field through technological democratization
Clik here to view.

2. Strategic Applications in Finance
Customer-Centric Innovations
- Hyper-personalized financial services
- Enhanced customer interfaces
- Proactive and predictive customer experience design
- Improved accessibility for underserved financial groups
Operational Efficiency
- Streamlined back-office operations
- Advanced risk management
- Automated complex decision-making processes
- Significant cost reduction and productivity enhancement
Clik here to view.

Security and Fraud Prevention
- Advanced anomaly detection beyond human capabilities
- Real-time identification of suspicious behaviors
- Sophisticated fraud prevention mechanisms
- Continuous learning and adaptation of security protocols
3. Competitive Dynamics
Organizational Adaptability
- Traditional financial institutions: Advantages of extensive data and resources
- Fintech startups: Agility and rapid AI solution deployment
- Success depends on strategic AI integration and innovation speed
Investment and ROI
- Substantial investments driving AI development
- An estimated 75%+ of leading organizations are already leveraging generative AI
- Clear return on investment across multiple business dimensionsImage may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.![]()
4. Broader Implications
Workforce Transformation
- Skill development becomes critical
- Emphasis on AI literacy and interdisciplinary technological understanding
- Redefinition of job roles and professional capabilities
Global and Sustainability Potential
- AI as a tool for addressing complex global challenges
- Potential for creating more inclusive and sustainable economic models
- Applications beyond finance (e.g., cultural soft power, multilingual communication)
Clik here to view.

5. Future Outlook
Regional Leadership
- Countries like Thailand positioning themselves as potential AI innovation hubs
- Focus on creating meaningful, impactful AI use cases
- Collaborative ecosystem between technology, business, and education sectors
Philosophical Perspective
- AI viewed as a catalyst for positive societal transformation
- Technology transcending mere operational improvement
- Potential to unlock unprecedented human potential and economic opportunities
Conclusion
The AI revolution in finance and business represents more than a technological trend—it’s a fundamental restructuring of how organizations operate, compete, and create value in an increasingly digital global economy.
Clik here to view.
AI Transformation in Singapore: Strategic Positioning and Opportunities
1. National Technological Ecosystem
Strategic Advantages
- World-leading financial hub with advanced technological infrastructure
- Strong government support for digital innovation
- Robust regulatory framework conducive to technological experimentation
- Highly skilled workforce with deep technological literacy
Clik here to view.

Key Differentiators
- Established as a global fintech and innovation center
- Significant government investments in AI and digital transformation
- Strategic geographical location bridging Asian markets
- Multicultural workforce enabling diverse technological perspectives
Clik here to view.

2. Financial Sector AI Applications
Banking and Financial Services
- Enhanced fraud detection leveraging advanced machine learning
- AI-driven personalized financial advisory services
- Automated compliance and risk management systems
- Intelligent customer interaction platforms
Fintech Innovation
Clik here to view.
- Sandbox environments for AI financial product development
- Support for AI startups through government grants and incubation programs
- Rapid prototyping and scaling of innovative financial technologies
- Cross-border financial technology collaborations
3. Competitive Strategy
Talent Development
- Comprehensive AI and digital skills training programs
- Collaboration between educational institutions and industry
- Attraction of global AI talent through progressive policies
- Continuous upskilling of existing workforce
Clik here to view.

Investment and Infrastructure
- Significant national investments in AI research and development
- Creation of dedicated AI innovation districts
- Public-private partnerships driving technological advancement
- Strategic focus on ethical AI development
4. Sectoral Transformation
Banking Sector
- DBS, OCBC, and UOB leading AI integration efforts
- Predictive analytics for customer insights
- Automated credit scoring and risk assessment
- Intelligent process automation
Government and Regulatory Support
Clik here to view.

- Proactive AI governance frameworks
- Incentives for responsible AI adoption
- Focus on maintaining global competitiveness
- Balancing innovation with data privacy and security
5. Global Positioning
Regional AI Hub Aspirations
- Competing with other Asian tech centers like Tokyo, Seoul, and Singapore
- Creating unique value propositions in AI financial technologies
- Developing cutting-edge use cases for global markets
- Positioning as a thought leader in responsible AI implementation
International Collaboration
- Active participation in global AI research networks
- Knowledge exchange programs
- Hosting international AI and fintech conferences
- Promoting Singapore as a neutral, innovative tech platform
6. Challenges and Considerations
Potential Barriers
- High implementation costs
- Cybersecurity risks
- Talent acquisition challenges
- Rapid technological obsolescence
Mitigation Strategies
- Continuous learning and adaptation
- Robust cybersecurity investments
- International talent attraction
- Agile technological frameworks
Conclusion
Clik here to view.
Singapore stands at the forefront of the AI transformation, with a unique combination of strategic location, government support, technological infrastructure, and innovative spirit. The nation is not just adopting AI but is actively shaping its global narrative in financial and business technologies.
Maxthon
Maxthon has set out on an ambitious journey aimed at significantly bolstering the security of web applications, fueled by a resolute commitment to safeguarding users and their confidential data. At the heart of this initiative lies a collection of sophisticated encryption protocols, which act as a robust barrier for the information exchanged between individuals and various online services. Every interaction—be it the sharing of passwords or personal information—is protected within these encrypted channels, effectively preventing unauthorised access attempts from intruders.
Maxthon private browser for online privacyThis meticulous emphasis on encryption marks merely the initial phase of Maxthon’s extensive security framework. Acknowledging that cyber threats are constantly evolving, Maxthon adopts a forward-thinking approach to user protection. The browser is engineered to adapt to emerging challenges, incorporating regular updates that promptly address any vulnerabilities that may surface. Users are strongly encouraged to activate automatic updates as part of their cybersecurity regimen, ensuring they can seamlessly take advantage of the latest fixes without any hassle.
In today’s rapidly changing digital environment, Maxthon’s unwavering commitment to ongoing security enhancement signifies not only its responsibility toward users but also its firm dedication to nurturing trust in online engagements. With each new update rolled out, users can navigate the web with peace of mind, assured that their information is continuously safeguarded against ever-emerging threats lurking in cyberspace.
Clik here to view.

The post AI Landscape in Financial Services: Singapore Context appeared first on Maxthon | Privacy Private Browser.
